Understanding Habitat Corridors
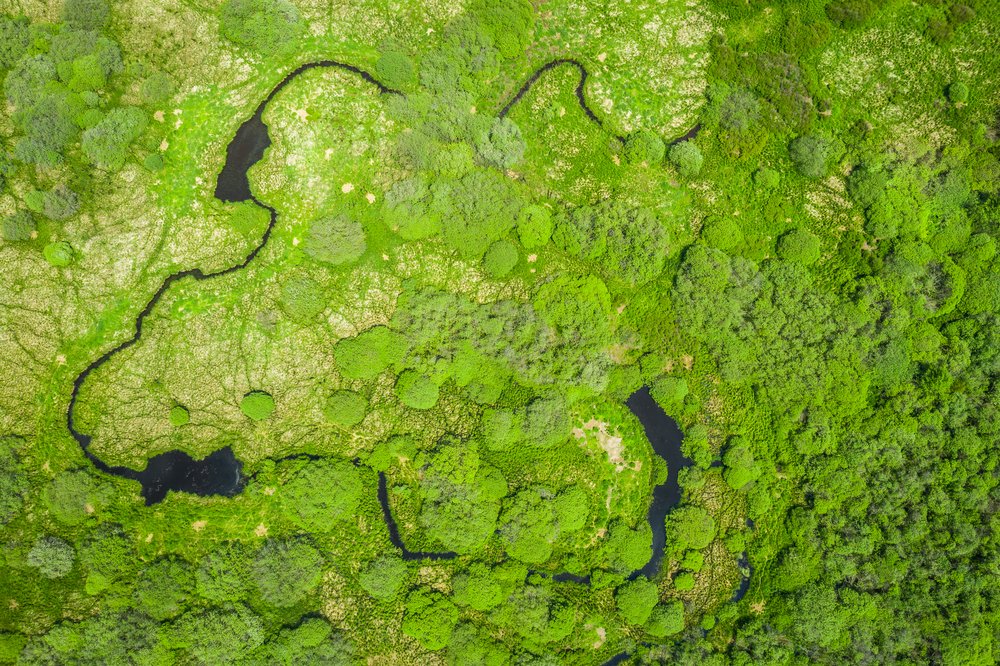

Habitat corridors, often referred to as wildlife corridors, are strips of natural habitat that connect separate populations of wildlife. These corridors play a significant role in conserving biodiversity by allowing animals, including big cats, to move safely between fragmented ecosystems. By providing this connectivity, habitat corridors help to maintain genetic diversity, stabilize populations, and support overall ecosystem health.
The Plight of Big Cats
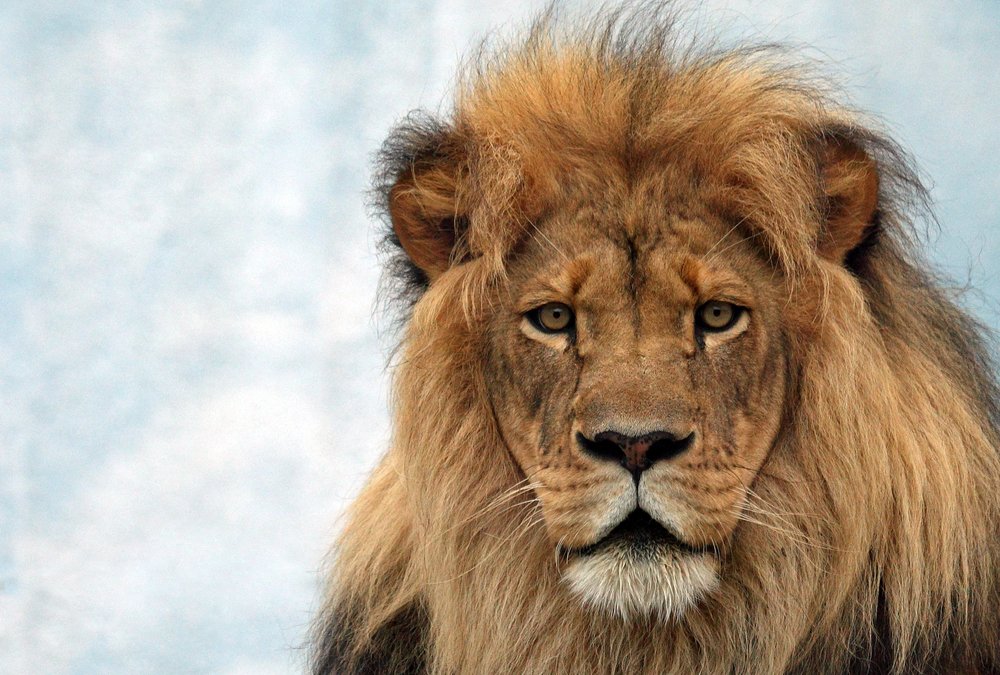

Big cats, such as tigers, lions, leopards, and jaguars, are apex predators critical to maintaining the balance of their ecosystems. However, they face numerous threats, including habitat loss, poaching, and human-wildlife conflict. As a result, many big cat species are now endangered or vulnerable, with some populations isolated due to fragmented habitats.
Impact of Habitat Fragmentation
Habitat fragmentation occurs when large, continuous areas of natural habitat are divided into smaller, isolated patches. This division is often due to human activities such as agriculture, urban development, and infrastructure projects. For big cats, this can lead to isolated populations that lack genetic diversity, making them more susceptible to diseases and decreasing their ability to adapt to environmental changes.
The Role of Habitat Corridors in Genetic Diversity

One of the primary benefits of habitat corridors is their role in maintaining genetic diversity. By enabling the movement of big cats between isolated populations, corridors allow for gene flow, which increases genetic diversity and resilience. This exchange is crucial for reducing the risk of inbreeding and ensuring the long-term survival of species.
Facilitating Migration and Movement
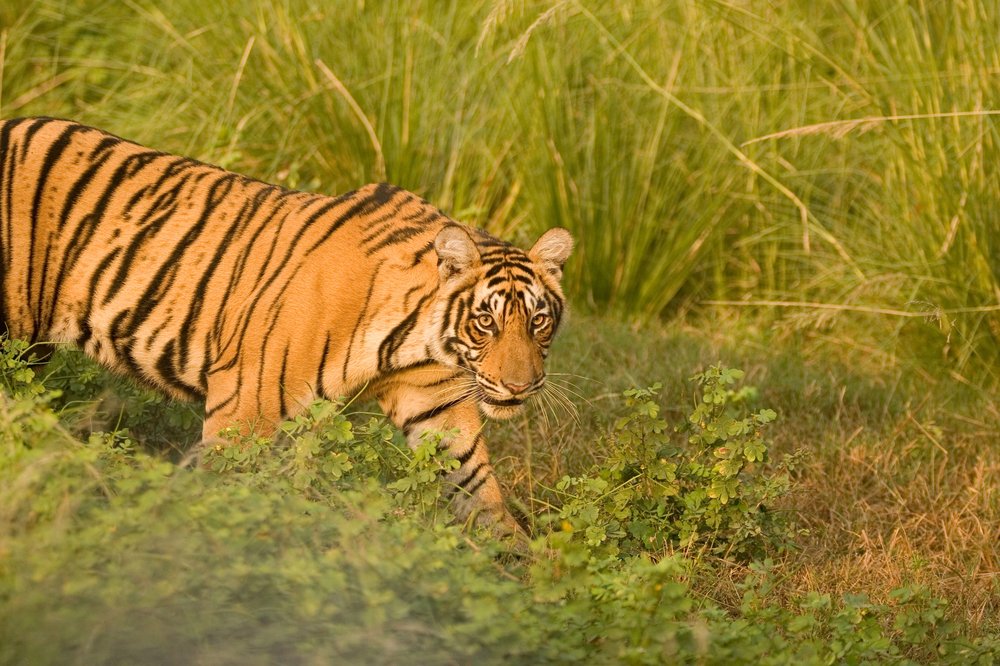

Big cats have large home ranges and require significant territory for hunting and breeding. Habitat corridors facilitate migration and movement across these ranges, allowing big cats to access different parts of their habitat to find food, mates, and breeding grounds. This mobility is essential for the daily survival and reproductive success of these animals.
Reducing Human-Wildlife Conflict

Habitat corridors can help reduce human-wildlife conflict by directing big cats away from human settlements and farms. By providing a natural path for movement, corridors reduce the likelihood of big cats venturing into human-dominated areas where conflicts often occur. This separation helps protect both wildlife and human livelihoods.
Promoting Ecosystem Stability

Big cats are keystone species, meaning their presence and activities have a significant impact on the structure and function of their ecosystems. By preying on herbivores, big cats help regulate prey populations, promoting vegetation growth and maintaining biodiversity. Habitat corridors ensure that big cats can fulfill this role across fragmented landscapes, supporting overall ecosystem stability.
Designing Effective Habitat Corridors

Creating effective habitat corridors requires careful planning and consideration of several factors, including the size, shape, and location of the corridor. Successful corridors mimic natural habitats and consider the specific ecological needs of the species they aim to support. Additionally, corridors should be kept free from significant human disturbances and should connect critical habitat areas.
Challenges in Implementing Habitat Corridors
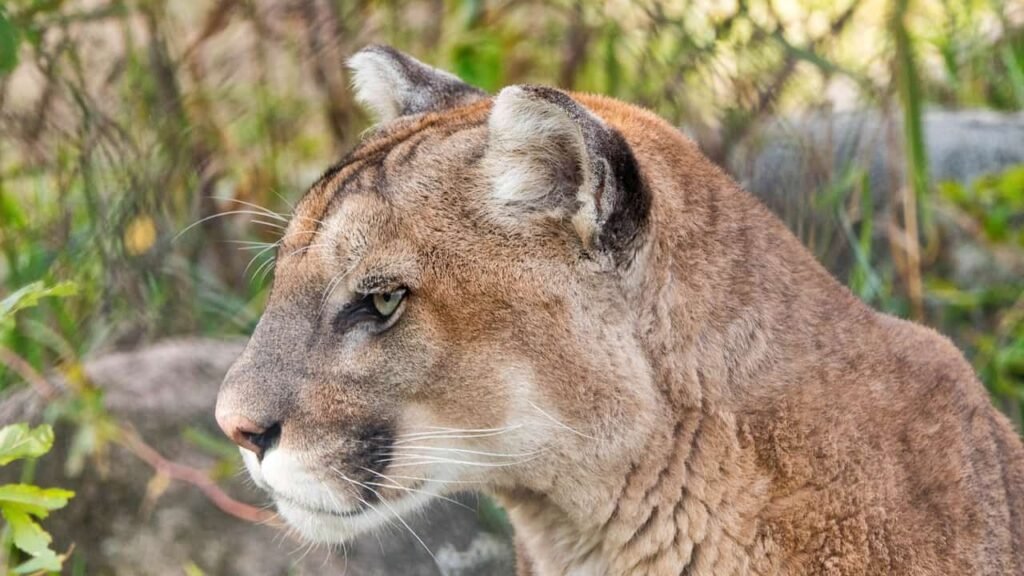

Despite their benefits, implementing habitat corridors poses several challenges. Land availability, funding, and political will are often limited, hindering the establishment and maintenance of corridors. Moreover, balancing the needs of wildlife with economic and developmental goals requires cooperation among multiple stakeholders, including governments, conservation organizations, and local communities.
Success Stories and Future Prospects
Several successful examples of habitat corridors exist around the world, demonstrating their potential to support big cat conservation. For instance, the Mesoamerican Biological Corridor aims to connect habitats across seven Central American countries, benefiting jaguars and other species. As awareness of the importance of habitat corridors grows, more initiatives are being developed, supported by advances in conservation science and technology.
Conclusion

The survival of big cats depends heavily on our ability to mitigate the impacts of habitat fragmentation. Habitat corridors offer a promising solution by enhancing connectivity between isolated populations, supporting genetic diversity, and promoting ecosystem stability. As we strive to conserve these magnificent predators, prioritizing the creation and maintenance of habitat corridors will be critical in ensuring their future in the wild.

Suhail Ahmed is a passionate digital professional and nature enthusiast with over 8 years of experience in content strategy, SEO, web development, and digital operations. Alongside his freelance journey, Suhail actively contributes to nature and wildlife platforms like Feline Fam, where he channels his curiosity for the Feline into engaging, educational storytelling.
With a strong background in managing digital ecosystems — from ecommerce stores and WordPress websites to social media and automation — Suhail merges technical precision with creative insight. His content reflects a rare balance: SEO-friendly yet deeply human, data-informed yet emotionally resonant.
Driven by a love for discovery and storytelling, Suhail believes in using digital platforms to amplify causes that matter — especially those protecting Earth’s biodiversity and inspiring sustainable living. Whether he’s managing online projects or crafting wildlife content, his goal remains the same: to inform, inspire, and leave a positive digital footprint.






